The Long Run Average Total Cost Curve Is Always
The LRAC curve is found by taking the lowest average total cost curve at each level of output. In the long run the total variable cost equals the total fixed cost.

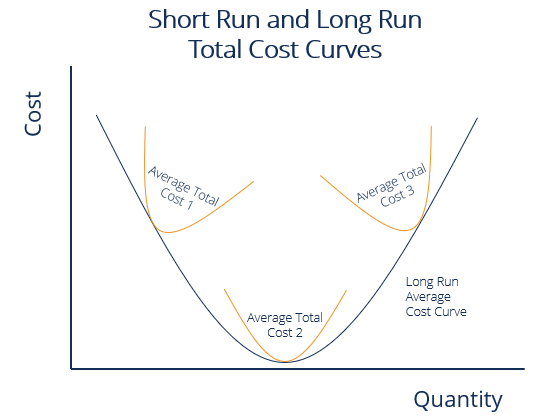
Reading Short Run And Long Run Average Total Costs Microeconomics
Long run Average Cost LAC is equal to long run total costs divided by the level of output.

. In the long run when marginal cost is below average total cost the average total cost curve exhibits a. In the long run the fixed cost remains unchanged and the variable cost only could influence the total cost. The long-run average cost curve is a planning device because this curve shows the least cost of producing each possible output.
If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. In the long run the firms fixed costs are greater than its variable costs. See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
B constant returns to scale. To estimate the long-run average cost LAC for a typical drug accounting for the effects of generic competition and medical cost offsets. Rising as output increases.
The long-run supply curve is always more elastic than the short-run supply curve. The long-run average cost curve envelopes the short-run average cost curves in a u-shaped curve. Flatter than the short-run average total cost curve but not necessarily horizontal.
When the fixed input in the SR is increased the SRATC will shift right. While the traditional shape of the Long-run cost curve is U shape the modern curve is more favourable to the L shape because technology allows for better optimization of new and old. The graph above shows 3 short run average total cost curves and their relationship to the long run average total cost curve.
Constant returns to scale Suppose a firm doubles its inputs therefore doubling its. A long run average cost curve is known as a planning curve. OQ is the optimum point because the output OQ is produced at the minimum point of the long run average cost curve and the corresponding SAC SAC 4.
B falling long-run average cost curve. The long-run average total cost curve is always a. The derivation of long run average costs is done from the short run average cost curves.
If the long-run average cost curve is horizontal it implies that the firm is experiencing _____. The long-run average total cost curve is always a. The long-run average total cost curve describes how average costs vary when all inputs can be adjusted.
Long-run average total cost LRATC represents the average cost per unit of production over the long run. The long-run average cost curve is used in most meetings where all operations of a firm are being considered and are in the process of being optimized for low cost and high returns. In this calculation all inputs are considered to be variable because over the long term no costs are considered fixed.
This problem has been solved. Here average total cost curves for quantities of capital of 20 30 40 and 50 units are shown for the Lifetime Disc Co. In the long run the average cost curve is always downward sloping.
Returns to scale can be determined by assessing if the long-run average cost curve is downwards sloping constant or upwards sloping at the quantity output. Falling as output increases. We estimated the LAC for a.
Thus the concept relevant to explain the shape of long run cost curve is the law of returns to scale. Managers therefore are normally faced with a choice among a wide variety of plant sizes. It envelopes all of the possible short-run average total cost curves.
Falling as output increases. Long run average cost is long-run total cost divided by the level of output. This is because a firm plans to produce an output in.
37 When a firm doubles its inputs and finds that its output has more than doubled this is known as. You can see that each short run average total cost curve intersects the long run average total cost curve at a specific point. Long run average cost curve depicts the least cost possible average cost for producing various levels of output.
In the short run the average total cost curve always lies above the average variable cost curve. Rising as output increases. Descriptive analysis of retrospective cross-sectional survey dataMethods.
As shown in the figure 43a the short run average cost curves which are also known as plant curves. A economies of scale. In the short run plant is fixed and each short run curve corresponds to.
In the long run all costs are variable costs. Long Run Average Cost. C constant long-run average cost curve.
In the short run the average total cost curve always lies above the average variable cost curve. Up to 256 cash back a rising long-run average cost curve. D rising then falling then rising long-run average cost curve.
Up to 24 cash back The long-run average total cost curve is always quizlet ABSTRACTObjectives. Figure 89 Relationship Between Short-Run and Long-Run Average Total Costs. As the level of output increases the economies of scale works and the average cost of production decreases initially.
The long-run average total cost curve is always flatter than the short-run average total cost curve but not necessarily horizontal true The length of the short run is different types of firms. In the long run the quantities of all inputs are fixed. Flatter than the short-run average total.
In the long term businesses can adapt and change elements of the production process for example by changing the supply chain but the. While other plants are used at less than or more than their full capacity only SAC 4 is operated at the minimum point. 4 rows The long-run average total cost curve is always.
Flatter than the short-run average total cost curve but not necessarily horizontal.

Long Run Average Total Cost Curve Video Khan Academy

Long Run Average Cost Curve Derivation Example Solved Questions Etc
Comments
Post a Comment